Sound Therapy for Tinnitus Relief: Legit or Bogus?

No Value (acf:field_669fe7fdb55ef)

The most defining symptom of tinnitus is a ringing, buzzing, or similar sound in your ears that no one else can hear. While the sound isn’t typically very loud or painful, it can be annoying and make enjoying conversation or listening to things like music, movies, and TV shows more difficult.
Tinnitus can have a significant impact on your daily life, so, naturally, people suffering from it seek out solutions or treatments that offer relief.
Doctors still haven’t pinpointed an exact cause of tinnitus, which makes it difficult to pinpoint a one-size-fits-all treatment. A variety of factors including hearing loss, ear injuries, infections, blockages, and medications are all potential contributors.
While there is no known cure for tinnitus, many people have found that sound therapy can offer some relief. But what is sound therapy, and is it actually effective?
What is tinnitus sound therapy?
Sound therapy is exactly what the name suggests: the use of specific sound frequencies to soothe or treat a problem. There are several forms of sound therapy that may be useful to people with tinnitus:
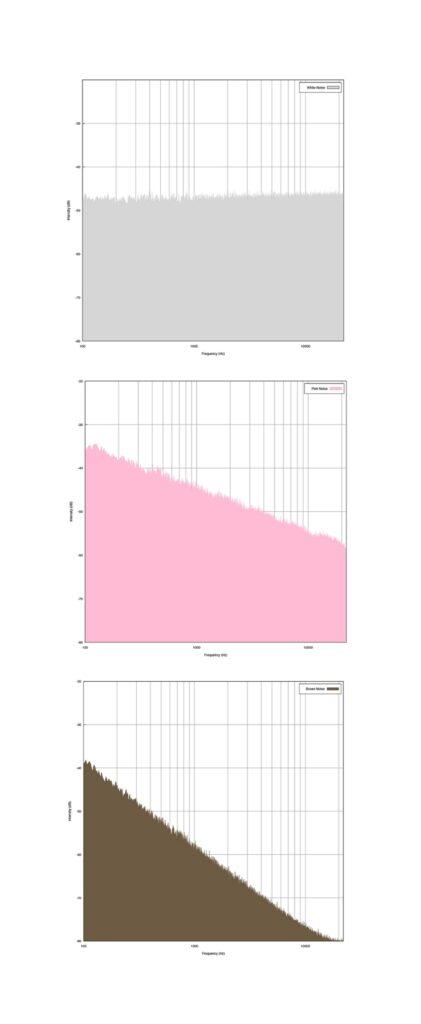
- The first is using tinnitus relief sounds — white, pink, or brown noise to cover, counter, or mix with the sound of your tinnitus. How can sounds be colors? The color names are simply a way audio engineers categorize sounds by which frequencies they emphasize. For example, white noise is an even distribution across all frequencies within human hearing, while pink noise slightly tunes down the higher frequencies, and brown noise amplifies low frequencies. Which “color” best suits your particular tinnitus sound may take some experimentation.
- Another type of sound therapy that may provide tinnitus relief is “notch therapy.” This involves creating unique audio tracks with specific frequencies removed, or “notched.” The idea is to target the specific frequency of your tinnitus sound and teach your brain to ignore it entirely.
Some hearing aid models come with settings specifically designed to mitigate tinnitus symptoms, often using variations of these sound therapy principles. People with hearing loss who also happen to experience tinnitus also may notice a reduction in their tinnitus symptoms when they have their hearing aids in.
Does sound therapy work for tinnitus?
So far, there have only been small studies on the effectiveness of sound therapy as a tinnitus treatment. However, those results have been encouraging.
- In a 2018 study, 72% of patients reported that 30 minutes of high-frequency sound therapy reduced their symptoms.
- A 2020 report determined that sound therapy may be effective in combination with cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT).
- A 2021 study found that one month of notched therapy produced measurable results in how the brain responds to the specified frequency.
All of these studies recommended more research. Ultimately, how you treat your tinnitus is up to you and your audiologist. However, if the ringing or buzzing in your ears is impacting your daily life, it may be time to ask your audiologist if they think sound therapy could work for you.
What other options for tinnitus treatment are available?
When it comes to treating tinnitus symptoms, sound therapy is far from your only option.
Counseling
With guided practice, you may be able to train your body and mind to ignore tinnitus sounds.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that helps you change how you think about tinnitus and reduce anxiety surrounding it.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is a behavioral therapy that encourages you to accept unwanted experiences.
- Mindfulness is a meditative practice that helps you be aware of sensations without judgement.
- Tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT) is an innovative approach that combines one or more of these counseling strategies with the sound therapy we discussed earlier in this article to help you tune out tinnitus.
Medication
Some medicines have proven effective in treating tinnitus symptoms and effects. If other treatment options aren’t as effective as you’d like, you can talk to your doctor about medication options. Tricyclic antidepressants can help reduce tinnitus symptoms in some patients and improve quality of life.
You can also consult your doctor about medications to treat tinnitus-related anxiety or depression. Similarly, some prescription sleep aids may help you overcome sleep disturbances associated with tinnitus.
Hearing aids
Most major hearing aid manufacturers have developed products specifically for tinnitus.
- Widex hearing aids equipped with Zen Therapy software, which projects calming fractal tones into your ears at irregular intervals, cutting through the monotonous tinnitus sound.
- Signia offers hearing aids programmed for Notch Therapy, which filters out the tinnitus pitch, teaching your brain to ignore sounds at that frequency over time.
- Phonak’s Tinnitus Balance Portfolio includes several devices that use a similar approach to help users tune out their tinnitus sound.
- Oticon hearing aids with Tinnitus SoundSupportTM can play white, pink, and brown noise for tinnitus relief.
- ReSound also offers a bank of broadband sounds, including white, pink, speech noise, and high-frequency noise.
- Starkey’s Multiflex Tinnitus Technology is an adjustable sound stimulus that you can customize with the help of a hearing specialist.
Work with your doctor or audiologist to find the solution or combination of solutions that best fits your lifestyle and your tinnitus needs.
Related articles
Deaf Community
News
News and updates about Sorenson VRS products and features and the Deaf community
Hearing Health Providers News
Hearing loss news and trends for hearing health professionals
Hard-of-Hearing
News
News and updates about living well with hearing loss and getting the most out of CaptionCall and CaptionCall Mobile

No Value (acf:field_67911dacbb423)

No Value (acf:field_67911d8bbb421)













































